Blood is made of four components:

Plasma
Plasma is a pale yellow sticky liquid. It makes up 55% of the blood’s volume. The components of plasma are water 92%, dissolved protein 8%, glucose, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, urea, uric acid, CO2, hormones, antibodies. Plasma carries dissolved materials such as glucose, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, salts, carbon dioxide, urea, and hormones. It also carries heat energy.
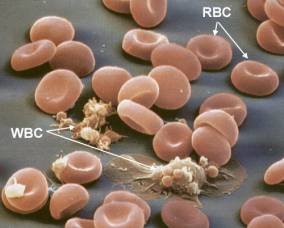
Red Blood Cells
Red Blood Cells, also called erythrocytes, are tiny biconcave disc-shaped cells. They do not have a nucleus or mitochondria. Their cytoplasm is rich in haemoglobin. O2 binds to the iron in haemoglobin. Red blood cells are made in the bone marrow. They survive for about four months. They are destroyed and recycled by the liver and spleen. They are destroyed because they have to constantly change shape to pass through narrow blood vessels. When they die the haemoglobin is stored in the liver and used to make new blood cells in the bone marrow. They are very small. There are about 5 million red blood cells in 1 cc. of blood. The rest that is not stored is converted into bile pigments.
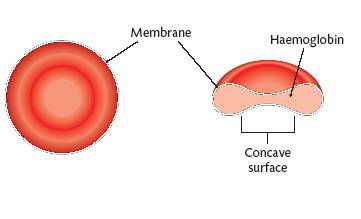
Red Blood Cells transport oxygen. Haemoglobin has a base of iron. The iron joins with oxygen in areas of high oxygen concentration (in the lungs and releases oxygen in areas of low oxygen concentration in the body cells.
Anaemia is the lack of haemoglobin or red blood cells. The symptoms of anaemia are pale skin colour and a loss of energy.
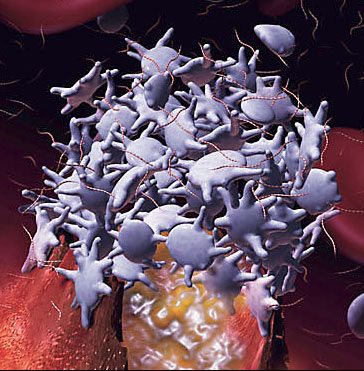
RED BLOOD CELL, PLATELET, WHITE BLOOD CELL:
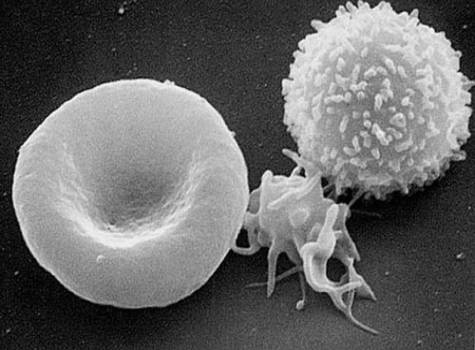
While Blood Cells
White Blood Cells (leucocytes) are colourless cells and possess a nucleus. They function in defending the body against pathogens. Some ‘feed’ on pathogens by phagocytosis. These white blood cells are called phagocytes. Others, the lymphocytes produce antibodies, the specific defense proteins. They are made by the bone marrow and lymphatic tissue.
A white blood cell ingests a pathogen by phagocytosis:
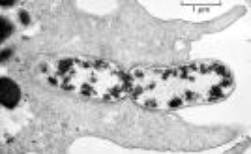
TYPES OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS
Lymphocytes:
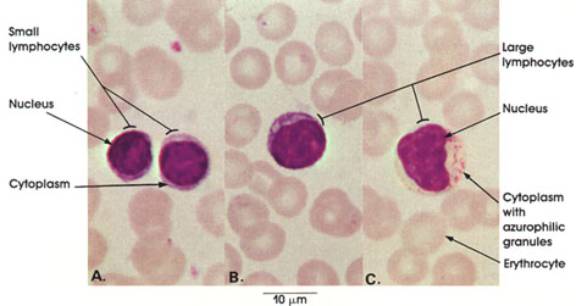
Lymphocytes are made in the bone marrow and then stored in various in various parts of the lymphatic system. Their main function is to make antibodies.
Monocytes:
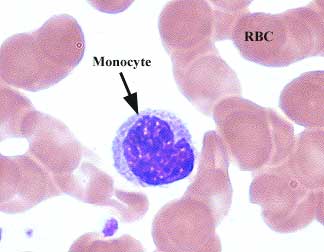
Monocytes are large cells that digest bacteria and other particles. They are also called macrophages. They have kidney shaped nuclei.
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are tiny fragments of large bone marrow cells. They carry specialised blood clotting chemicals. The clotting chemicals are released where blood and lymph vessels are injured. A nucleus is not present in platelets.
These platelets are grouping at the site of a wound: